Aluminum alloy die casting is a die casting process that is a widely used process in manufacturing that involves producing accurate and intricate parts of metal with efficiency. In this case, we can list metals that have a variety of applications due to their capacity to be very strong and light simultaneously. Besides this, we can list that practically corrosion-resistant, i.e., aluminum alloys are particularly popular with car manufacturing. This article also looks into such areas as processes, properties, challenges, and applications of aluminum alloy die casting. We will get deep insights into its complete process, types, and differences from other processes.
What is Die Casting?
It is a manufacturing process that utilizes high pressure to force a molten metal to fill a mold cavity. It also allows the generation of excellent models with near-net shaping, accurate dimensions surface finish, and complicated shapes.

Different Types of Die Casting
Die-casting has many types. Let’s discuss these types in detail;
1. Hot Chamber Die Casting
It is mostly suitable for zinc and magnesium alloys. This process takes submergence of the injection system in the molten metal to facilitate rapid casting. It is ideal for use in a large production but unadapted for utilization in high-melting-point alloys. you can go to zinc die casting to know more detail
2. Cold Chamber Die Casting
It is a best fit for metals such as aluminum and brass having high melting points. Here we transfer the molten into a cold chamber and then inject it into the mold. It saves on the heat hazard to the equipment but has longer operating cycles. Got aluminum die casting services page to know more about this process.
3. Low-Pressure Die Casting
The low-pressure die casting use with Used with aluminum and magnesium alloys. It causes minimal porosity but good structural quality. Besides this, it is time-consuming but suitable for creating the stronger part of the product.
4. High-Pressure Die Casting (HPDC)
Common in aluminum, zinc, and magnesium alloys. Here we inject the molten metal at very high pressure into complicated shapes and fine surface textures. So, it is highly suitable for applications that need parts with large production quantities, and areas with large cross-sections may be porous. Go to high pressure die casting page to know more detail.
5. Gravity Die Casting
Standing pressure is used to cast molten metal into a mold thus yielding strong and low porosity objects. It is used in production lines where we need to produce less number of parts at a time but it is comparatively slower than pressure-based processes.
7. Squeeze Die Casting
Here we make semi-finished products by the pressure forging method where molten metal is high pressure and can also prevent casting porosity. This is suitable for the structure of a part; however, it has a higher cost and slow cycle time.
Define Aluminum Alloy die casting
Aluminum alloy die casting is a process in which molten aluminum alloy materials are forced under pressure into molds or dies. So, it can form the desired shape and a very smooth surface finish. It is employed in component manufacturing with complicated shapes that require high strength, stiffness, and low density integrated with good surface finish and accurate dimensions. The aluminum alloy has all the favorable characteristics of high corrosion and heat transfer coefficients and hardness-to-weight ratio. One of the benefits of this process is that die casting is suitable for large-scale production processes.

Selecting the Right Material for Aluminium alloy Die Casting
Materials used are very vital in the aluminum alloy die-casting business since they determine the efficiency, quality, reliability, and cost of the final product. Properly chosen alloys ensure:

- Strength and Durability: Products have to sustain working loads.
- Thermal and Electrical Performance: Closely associated with thermal conductivity and dissipation.
- Corrosion Resistance: Essential for searches that relate to outdoor and marine product or service-related searches.
- Castability: Minimises production distortions with fewer defects.
- Machinability and Finishing: It ensures a reduction of the complexities of the post-casting processes.
- Cost Efficiency: Achieves performance concerning the implementation of the budget.
- Sustainability: Such alloys can minimize and even cause negativities to the environment.
Aluminum alloys in die casting
Die-casting aluminum alloys are common to many industries because these materials possess qualities that are desirable in dies such as lightweight, high strength, and corrosion resistance.
| Alloy | Key Properties | Applications | Values |
| A380 | Strong, corrosion-resistant | Engine blocks, housings | Strength: 320 MPa |
| A383 | Crack-resistant, castable | Electronics, thin parts | Strength: 290 MPa |
| A360 | Corrosion-resistant, durable | Marine, aerospace | Strength: 330 MPa |
| ADC12 | Castable, corrosion-resistant | Automotive, machinery | Strength: 310 MPa |
| AlSi9Cu3 | Strong, wear-resistant | Structural components | Strength: 250–280 MPa |
Complete Process for Aluminum Alloy Die Casting
Aluminum die casting entails the formation of elaborate and accurate first parts by the application of pressure on molten aluminum alloys. Below are the key stages:
1. Mold Preparation
- Die Design: A reusable steel mold (die) is preplanned and accurately carved to meet the form and function of a particular just manufactured part.
- Die Preheating: One is to heat the mold to minimize thermal shock and hence facilitate the flow of metal.
- Lubrication: Lubrication is used to avoid sticking and facilitate easy removal of some parts.
2. Melting and Alloy Selection
The aluminum alloys are brazed at a temperature of about 660 centigrade (1220 Fahrenheit) in a furnace. This aluminum is then kept at a relatively constant temperature to retain the material properties of the metal.
3. Injection
- Hot Chamber Die Casting: In the case of low melting alloys (which are comparatively rare in the case of aluminum).
- Cold Chamber Die Casting: The molten aluminum is then transferred on tow and poured into a cold chamber of the aluminum alloy forging press where it is injected at high pressure of between one thousand, five hundred to twenty-five thousand pound-force.
When high pressure is used, it ensures that the molten aluminum flows right to the small crevices resulting in excellent finishes.
4. Cooling and Solidification
It is the process during which the obtained molten aluminum cools and solidifies inside the given mold. Cooling minimizes defects such as shrinkage or warping that are brought about by dryness in the cast iron.
5. Ejection
Finally when the casting is fully formed its mold is ejected from the casting using the ejector pins. The mold is then ready for the next cycle of use with the Epicor software.
6. Trimming and Finishing
If necessary, runners, gates, and flash are removed from the casting leaving only the necessary shape and form of the object. Some of the operations include giving the required surface finishes such as sandblasting, polishing, or coating.
Die Casting Aluminum Alloy Properties
So, let’s discuss some of the important mechanical, chemical, and thermal properties of Aluminum alloy Diecasting;
I. Mechanical Properties
These may include;
- High strength-to-weight ratio: Perfect for those industries where weight and strength are critical parameters, such as automotive and aerospace industries.
- Good tensile strength: Permits alloys to be resilient to high-stress conditions.
- Excellent fatigue resistance: Promises reliable performance in dynamic as well as cyclic applications.
II. Thermal Properties
The following are some thermal properties of diecasting aluminum alloy;
- Good thermal conductivity: However, seen as a positive attribute of materials in usage such as in heat exchangers as well as engine parts where heat transfer is desired.
- Good heat resistance: Applicable to components subjected to high temperatures as used in engine blocks and auto parts.
III. Chemical Resistance:
These are generally;
- Corrosion resistance: Especially in such grades as A360, these alloys have relatively good behavior in severe conditions.
- Good oxidation resistance: Keeps the surface of external components, susceptible to moisture and corrosive influences, unaffected and safe for the outdoors or marine use.
These characteristics make aluminum alloys a premium material for die casting whose products are effective in different sectors.
Design Guide for Aluminum Alloy Die Casting
Design guide and material selection, both features play an important role in aluminum diecasting. So, let’s discuss the design guide properly;
| Design Factor | Guideline | Reasoning |
| Wall Thickness | Keep uniform thickness (2–4 mm) | Prevents defects like shrinkage and ensures uniform cooling. |
| Draft Angles | Use 1-3° draft on vertical surfaces | Aids in mold release and part ejection. |
| Radii and Fillets | Use rounded corners (0.5-2 mm radius) | Reduces stress and improves flow. |
| Gate Location | Position gates at thicker sections | Ensures uniform filling and reduces defects. |
| Parting Line | Place along flat surfaces | Minimizes visible marks and optimizes alignment. |
| Ejection System | Evenly distribute ejector pins | Ensures uniform ejection and prevents part distortion. |
| Tooling Considerations | Use guide pins and sprue systems | Ensures accurate mold alignment and metal flow. |
| Undercuts | Minimize undercuts or use side cores | Simplifies mold design and reduces costs. |
| Tolerances | Specify ±0.1 mm to ±0.3 mm for standard parts | Balances precision with cost efficiency. |
| Surface Finish | Choose appropriate finishes (e.g., smooth, sandblasted) | Enhances aesthetics and reduces post-processing. |
Key Features of Aluminum Alloys Used in Die Casting
Here are some of the important characteristics of the aluminum alloy we use;
- Lightweight: These alloys have a high strength-to-weight ratio. So, they have a range of applications in the automotive industries and aircraft industries.
- Corrosion Resistance: Natural oxide layers also give protection from rust and other factors that are not conducive to a product’s life span.
- High Thermal and Electrical Conductivity: They are as a result ideal in applications that require heat dissipation and good electrical systems such as electronic and engine parts.
- Excellent Castability: Aluminum alloys also have good flow characteristics, allowing more of the material to flow into the mold’s detail, which cuts down on defects and lets designers achieve smaller details with ease.
- Recyclability: Aluminum can be recycled almost indefinitely and there’s no loss in properties, which is good for sustainable production.
Comparison of Aluminum Die Casting with Other Manufacturing Processes
The following table gives us a descriptive overview of Aluminum diecasting and another manufacturing process. It gives the major comparison between all the processes;
| Property | Aluminum Die Casting | Sand Casting | Injection Molding | Forging |
| Material Used | Aluminum alloys | Various metals, including aluminum | Thermoplastics, thermosets | Metals (steel, aluminum, etc.) |
| Production Speed | High, suitable for mass production | Moderate, slower than die-casting | Very high for thermoplastics | Moderate, depending on the complexity |
| Part Complexity | High-complexity, thin-walled parts | Limited complexity, rougher surface finish | High complexity, fine details | Simple shapes, less complex than die-casting |
| Surface Finish | Smooth, can be improved with finishing | Rough, may require finishing | Excellent, fine finish | Rough, requires finishing |
| Tolerance | High precision, ±0.1 mm to ±0.3 mm | Lower precision requires machining | Very high precision | Moderate to high precision |
| Cost | High initial tooling cost, low unit cost for mass production | Low tooling cost, higher unit cost for low volumes | High tooling cost, low cost per part in mass production | Moderate to high, depending on material and complexity |
| Strength | High strength-to-weight ratio | Lower strength, suitable for low-stress applications | High for certain plastics, moderate for metals | High strength, especially for structural parts |
| Applications | Automotive, aerospace, electronics | Large parts, low-stress applications | Consumer goods, medical devices, automotive | Structural components, heavy machinery |
| Material Wastage | Low, efficient material use | High, due to sand mold waste | Low, especially for thermoplastics | Low, minimal waste compared to casting |
High Pressure Die Casting Aluminum Alloys
High-pressure die casting (HPDC) is the widely used technique in the aluminum alloy die-casting process. It entails the forced and rapid pouring of molten aluminum alloy into a steel cavity via high pressure.

Benefits of HPDC with Aluminum Alloys
- Precision and Complexity: Creates thin and delicate patterns with close-dimensional control.
- Surface Finish: In this case leads to surfaces with less roughness hence less machining is done on the final product.
- Efficiency: Enables ramp-up and high-speed manufacturing, low cycle time.
Use of HPDC Aluminum Alloys
- Automotive Industry: Car engines, gearboxes, and wheels.
- Electronics: Heat sinks, enclosures, and connectors.
- Aerospace: Wind blades for wind turbines, aircraft components, automotive components, and consumer goods.
Pros of aluminum alloy die casting.
So, here are some of the main advantages of aluminum diecasting;
- High Precision and Complex Designs: Aluminum alloys can be poured into molds and kinds of complex shapes and detailed parting lines, which are incorporated in the designs.
- Good Surface Finish: The die-cast aluminum parts are generally very shiny and tapered thus little or no post-casting treatment such as polishing or finishing is required.
- Lightweight and Strong: Aluminum alloys are lightweight, and this property fulfills the requirements of industries that have a concern about weight such as automobile and aircraft industries.
- Excellent Corrosion Resistance: Of all available materials, aluminum alloys are among the least prone to corrosion, which is good news for both outdoor and marine settings.
- Cost-Effective for Mass Production: After the mold is made die casting is one of the more cost-effective methods for mass production making per-part costs.
Cons of Aluminum Alloy Die Casting.
Among the most common problems associated with using aluminum alloy die casting are the following:
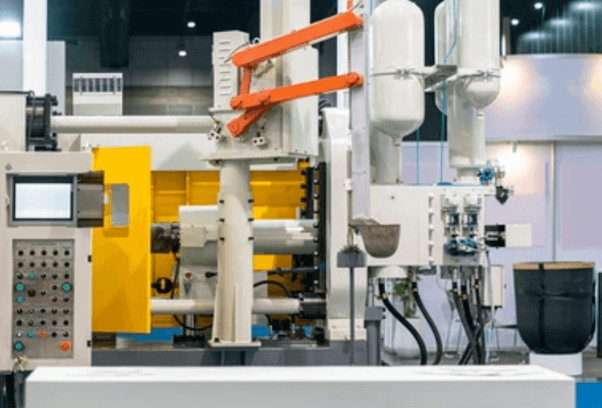
- High Initial Tooling Cost: This often means that the cost related to creating the die can be high and not very sustainable for a small volume of production.
- Limited Strength at High Temperatures: Similar to most non-ferrous alloys of wrought metals, aluminum alloys are not suitable for applications where high temperatures are used like steel materials.
- Porosity Issues: Porosity or voids are typical of aluminum die casting and may alter the mechanical characteristics of the finished part.
- Restricted to Thin-Walled Designs: Aluminum die casting is more appropriate for thin-walled parts, and therefore, it has bad prospects in heavy-throw, thick sections.
- Post-Casting Operations: Some parts may just need some finishing, and this will add to both the time and cost of production.
Applications Of Aluminum Alloy Die Casting
Let’s discuss the application of this process at the industrial scale;
- Automotive Industry: Applicable in the production of small engine parts such as cylinders, transmission housing, and other parts where there is a need for high strength and at the same time, low weight.
- Aerospace: They are also applied to aircraft parts like brackets, housing, and structural parts, and will provide lightweight with high-strength solutions to suit aerospace applications.
- Electronics: Aluminium die castings are used in the housing of consumer electronics products which include laptops computers, mobile handsets, and power supply units for protection and heat sinks.
- Marine: Parts including pumps, housing, and electrical enclosures for application in marine environments where corrosion is highly significant.
- Industrial Equipment: Machinery and industrial equipment use die-cast aluminum for gears, housing, and other applications due to the strength of the material.
Challenges Occur During Aluminum alloy die casting
Nevertheless, die casting using aluminum alloys has its problems of concern.
Common Issues
These issues may include;
- Porosity: Porosity of the gases can take place while casting and it results in the formation of voids in the material.
- Surface Defects: Some defects such as cold shuts and flow lines may however be present.
- Dimensional Instability: Some degree of shrinkage during cooling may be to blame for variations in the degree of tolerance.
Solutions
- Vacuum Die Casting: Decreases porosity since it removes entrapped gases.
- Optimized Gating Systems: It facilitates the proper flow of molten metal into the mold, thus playing a key role in the casting process.
- Post-Casting Treatments: Heat treatments enhance the mechanical characteristics and utilize dimensional stability.
Environmental and Economic Advantage
Here are some of the important environmental and economic advantages of Aluminum alloy diecasting;

I. Recyclability
Aluminum being a recyclable material is easily recyclable without many losses of properties. It also decreases the level of pollution and helps the organization to become environmentally friendly.
II. Cost-Effectiveness
The die-casting technique is cost-effective since it is more efficient and aluminum alloys are more recyclable than other materials.
III. Energy Efficiency
The utilization of light aluminum parts allows for energy saving in applications such as automotive and aerospace thereby helping to minimize emissions of carbon.
Technological Advancements in Die Cast Aluminum Alloys
Die casting is an expanding industry with the development of new forms and cast materials and techniques.
New Alloy Developments
- Stronger and less corrosive alloys than the existing ones.
- Specialty alloys are designed for certain industries for instance electric vehicle industry.
Emerging Technologies
- Additive Manufacturing: May be used together with die casting to produce a range of hybrid processes for difficult shapes.
- Automation: Improves productivity and accuracy of the die-casting cycle.
- Simulation Software: Predict casting defects and optimize the design of the cast.
Future Trends
- Higher demand for aluminum alloys because of their presence in electric cars.
- The manufacturing of high-performance, lightweight materials is required due to new environmental standards.
- Implementation of the intelligent production system for continuous quality monitoring.
Conclusion
Aluminum alloys are relatively new in the die-casting industry. It has brought about a lot of changes due to the many benefits they come with. So long as car makers, aerospace engineers as well as manufacturers of electronics demand lightweight and high-strength materials. So, they can use them in car frames, aircraft parts, and electronic gadgets respectively. Here the use of aluminum alloy die casting will continue to rise. As technology develops and becomes more sophisticated, the prospects of aluminum die-casting alloys continue to look even brighter. This unique material and processes are the most significant means for manufacturing in the future.
FAQs
Why are aluminum alloys chosen when it comes to die casting?
They are relatively light and can also resist corrosion, besides having a high strength-to-weight ratio so they are used widely in many industries.
Which die-casting types can be distinguished?
There are three principal categories: high-pressure die casting, low-pressure die casting, and gravity die casting which are applicable for various uses.
Which type of aluminum alloys are used in die casting?
Examples of these are A360, A380, and ADC12 that is widely used for their strength and casting capability.
What are the characteristics of aluminum alloys used in die-casting process?
Other features include tensile strength, elongation, and high-temperature resistance features to afford strength and reliability.
In what ways does aluminum die-casting reduce the impact on the environment?
Aluminium is a highly recyclable material and a light product that creates energy efficiency, especially in the automotive and aerospace industries.
What are the weaknesses in aluminum die casting and how can they be solved?
Such difficulties as porosity and surface roughness can be minimized by vacuum die-cast and testing of the gating system.